Services
Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) is a complete medical science with its own theory of how human physiology functions, its own diagnostic techniques, and treatment modalities which include acupuncture and herbal prescriptions.
Initial Exam
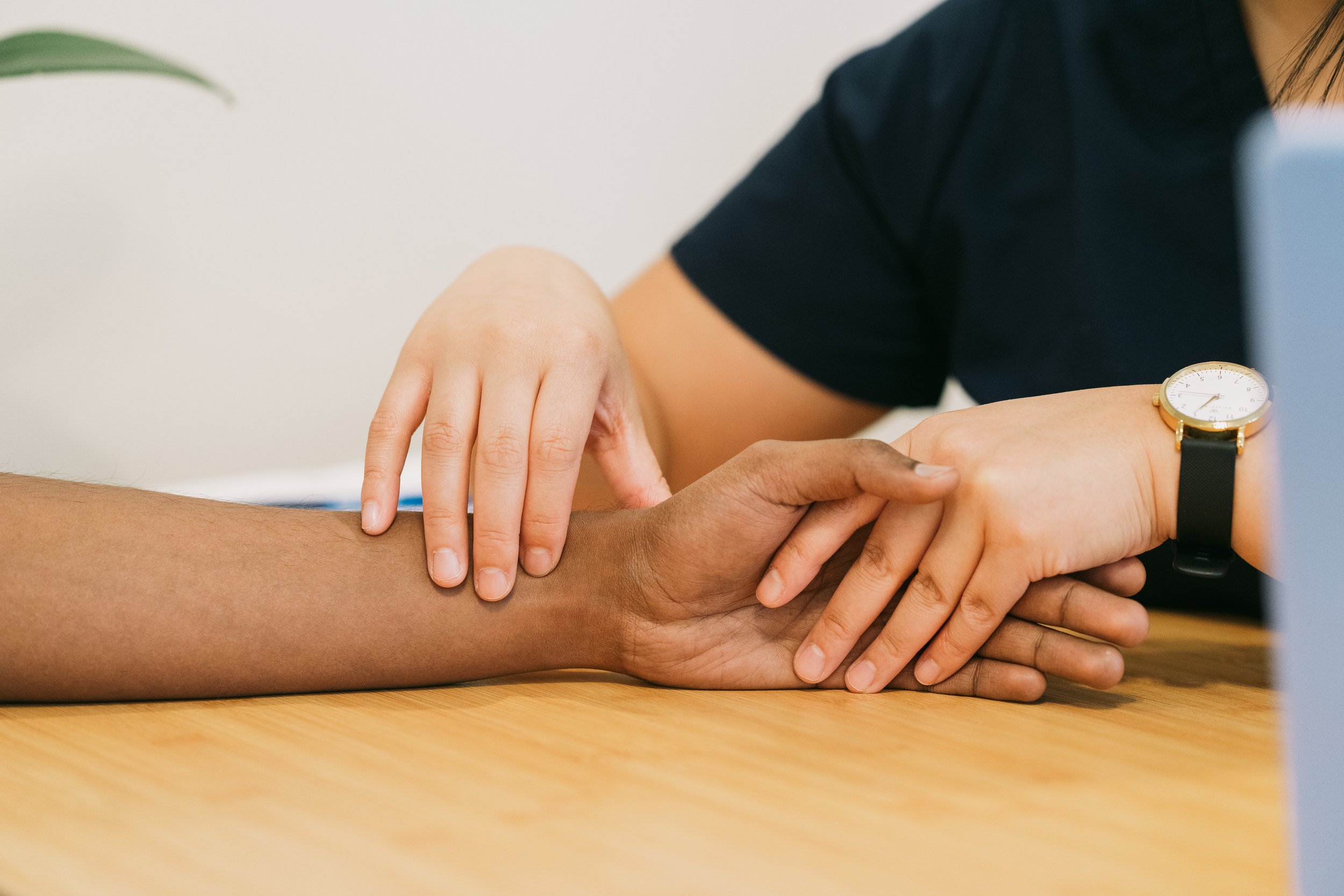
The first thing we do is put each patient through a thorough initial exam to figure out the why behind each individual condition or injury.
We practice whole body medicine, so we will go over the intake forms and conduct a detailed health history intake questionnaire and physical examination. Then if necessary, we exam the tongue and pulse.
For orthopedic conditions, we use a combination of muscle testing, orthopedic testing, range of motion testing, and an assessment of the individual’s mechanics to determine what muscles are creating the problem or inhibited due to injury.
Acupuncture
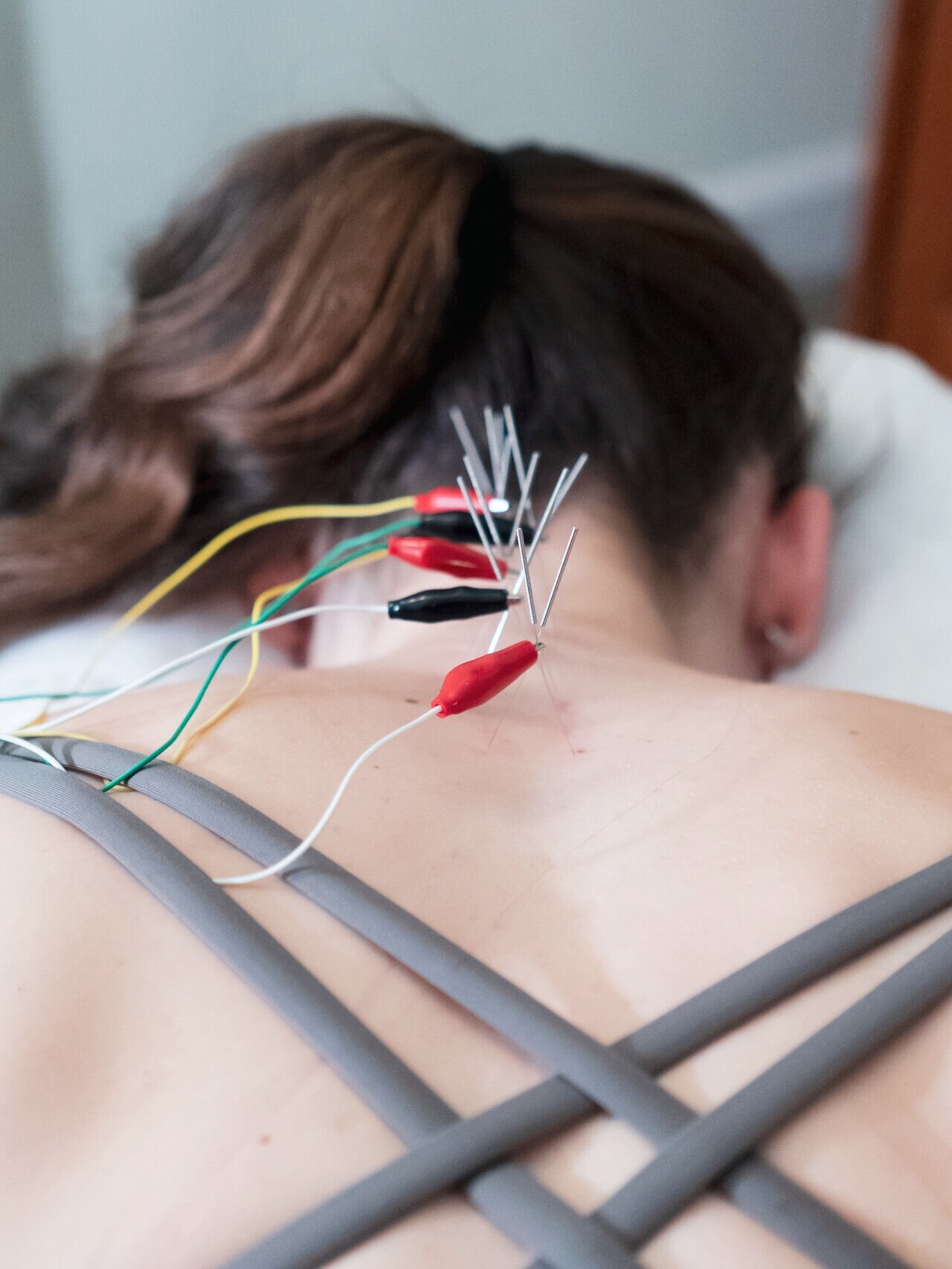
Acupuncture is a classical treatment used to optimize organ function, regulate the nervous system, and stimulate the body’s innate healing capacities. Acupuncture inputs new information into the body-mind system and can create both incredibly specific changes to musculature, the brain, and organs as well as broad stimulation of the relaxation pathways of the brain, a homeostatic effect on the immune system, and powerful effects on the endocrine (hormonal) system.
Treatments involve the insertion of sterile hair-fine needles, application of heat to specific points, and manual manipulation of channel pathways along the body. After a session, the points treated continue to activate. Acupuncture can also be used for direct muscle stimulation and to stimulate trigger points to eliminate pain and inflammation and reset muscle tone.
Cupping & Gua Sha
Cupping therapy uses glass or plastic cups, which are then placed on the skin to create negative pressure/suction and help release fascial adhesions and promote blood circulation. By creating space for blood and lymph flow, cupping helps loosen tight muscles and helps promote healing by “moving suck blood.” In turn, fresh nutrients are forced into the musculature and tissues. It can resolve long-term chronic injuries, aching muscles, and can help speed up the course of colds and flus. Depending on the specific condition, cups may be left stationary on the body for several minutes or may be moved around a larger area of the body.
Gua sha is an ancient pain-relieving technique where a tool, such as a piece of stone or a ceramic spoon, is scraped against the skin to create petechiea, or raised red or purple spots caused by broken blood vessels. On a physiological level, gua sha increases blood circulation in the local area and can help stretch fascia and break up adhesions. It resolves spasms and pain, and promotes normal circulation to the muscles, tissues and organs, as seen in Gua sha's immediate effect on coughing and wheezing. Research has shown that Gua sha causes a four-fold increase in microcirculation of surface tissue and can reduce inflammation and stimulate the immune system. Gua sha is similar to the precursor to the modern Graston technique.
Both cupping and gua sha active marks can last from a few days to a week dependent on the severity of one’s condition. Soreness is also expected in some cases, which can last up to 24-48 hours.
Chinese Herbal Medicine
Many people today are more open-minded to herbal medicine due to the adverse side effects of Western pharmaceuticals.
Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) is a complete medical science with its own theory of how human physiology functions, its own diagnostic techniques, and treatment modalities which include acupuncture and herbal prescriptions. The cornerstone of TCM is Chinese herbology, which has a 3,000-year history of continual evolution and success. Chinese medicine observes for patterns of ill health and treating them successfully.
Unlike the generic herbal supplements or balms that you buy at a vitamin store or health food store, we offer customized Chinese herbal formulas or specific topicals for our patients’ needs. Herbs are very powerful, but to be effective they must be prescribed on an individual basis. Generic herbal supplements have a ‘hit or miss’ effectiveness. The important thing with herbs is a proper diagnosis and an individualized prescription.
Sports Acupuncture & Dry Needling
Sports acupuncture was developed with the understanding of neurology and the functions of muscles. The first step to treatment with acupuncture is an assessment of which muscles may be contributing to the condition. Once this is defined, we are able to find the points in which nerves meet those muscles, known as motor points. When an acupuncture needle is used on a motor point with an electric impulse, it creates a contraction and relaxation phase releasing tight contracted bands of muscle. This is like hitting a reset button on the muscle. The results are immediate pain relief and improved muscle contractibility and mobility.
Dry needling uses a small, solid filament needle which is inserted into a painful contracted and knotted muscle to create a local twitch reflex. This is both diagnostic and therapeutic as it is the first step in breaking the pain cycle – as research shows, it decreases muscle contraction, reduces chemical irritation, improves flexibility, and decreases pain. In addition, when a needle is inserted into a muscle, it produces a controlled lesion and cuts between 3,000 and 15,000 individual muscle fibers. The body considers the needle a foreign invader and will activate the immune system as a response. The cut muscle fibers also produce an inflammatory reaction that the body responds to not just locally, but all over the body to reduce inflammation systemically.
Neurofunctional Acupuncture
Neurofunctional acupuncture, or electro stimulation, treatments are easy to replicate using a neurofunctional diagnostic approach. A neurofunctional diagnostic approach does not seek a single hypothetical source of pain; instead it investigates, clinically, the most common levels of dysfunction associated with a given pain problem, namely neurological, biomechanical, muscular, metabolic, and psycho-emotional levels.
Clinical examination aims to determine which muscles are neurologically inhibited and which are weak due to atrophy, which tissues have lost normal texture, which kinetic chains are not working properly, and which peripheral nerves have developed mechanosensitivity, among other things. Understanding all these aspects allows the practitioner to design a truly individualized integrated neurofunctional acupuncture treatment plan. Specifically, neurofunctional acupuncture interventions aim to facilitate modulation of neurological activity at every level identified as having been disturbed, such as autonomic sympathetic and parasympathetic, motor and sensory somatic, and central (autonomic centers, somatic areas, limbic system, cerebellum, etc.).
Source: Dr. Alejandro Ellelorega
Manual Therapy
Manual therapy, also known as “tuina”, is utilizing skilled, hands-on techniques to treat soft tissue and joints in order to reduce pain, increase range of motion, decrease myofascial restrictions to improve muscle length, decrease swelling or inflammation, assist the body in muscle or soft tissue repair, extensibility and/or stability, and facilitate movement to improve function. It’s often paired after acupuncture to round out the treatment, or pre- to desensitize those who are hypersensitive to needles.
For internal medicine organ imbalances, manual techniques are used to gently move important organ structures themselves (e.g., lungs, heart, liver, stomach) and the fascia (connective tissue) that surrounds them to improve the mobility of the organ, improve blood flow, and help the organ function more effectively.
Here in the clinic, we use a mix of hands only and instrument-assisted devices like the hypervolt, which provides vibration/percussion techniques for soft tissue issues.